vlinalg¶
-
torchvectorized.vlinalg.vSymEig(inputs: torch.Tensor, eigenvectors=False, flatten_output=False, descending_eigenvals=False)¶ Compute the eigendecomposition
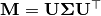 of every
voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.
of every
voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.Parameters: - inputs (torch.Tensor) – The input tensor of shape Bx9xDxHxW, where the 9 channels represent flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices.
- eigenvectors (bool) – If
True, computes the eigenvectors. - flatten_output (bool) – If
Truethe eigenvalues are returned as: (B*D*H*W)x3 and the eigenvectors as (B*D*H*W)x3x3 otherwise they are returned with shapes Bx3xDxHxW and Bx3x3xDxHxW respectively. - descending_eigenvals (bool) – If
True, return the eigenvvalues in descending order
Returns: Return the eigenvalues and the eigenvectors as tensors.
Return type: - Example:
import torch from torchvectorized.utils import sym from torchvectorized.vlinalg import vSymEig b, c, d, h, w = 1, 9, 32, 32, 32 inputs = sym(torch.rand(b, c, d, h, w)) eig_vals, eig_vecs = vSymEig(inputs, eigenvectors=True)
-
torchvectorized.vlinalg.vExpm(inputs: torch.Tensor, replace_nans=False)¶ Compute the matrix exponential
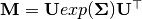 of
every voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.
of
every voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.Parameters: - inputs (torch.Tensor) – The input tensor of shape Bx9xDxHxW, where the 9 channels represent flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices.
- replace_nans (bool) – If
True, replace nans by 0
Returns: Return a tensor with shape Bx9xDxHxW where every voxel is the matrix exponential of the inpur matrix at the same spatial location.
Return type: - Example:
import torch from torchvectorized.utils import sym from torchvectorized.vlinalg import vExpm b, c, d, h, w = 1, 9, 32, 32, 32 inputs = sym(torch.rand(b, c, d, h, w)) output = vExpm(inputs)
-
torchvectorized.vlinalg.vLogm(inputs: torch.Tensor, replace_nans=False)¶ Compute the matrix logarithm
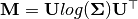 of
every voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.
of
every voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.Parameters: - inputs (torch.Tensor) – The input tensor of shape Bx9xDxHxW, where the 9 channels represent flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices.
- replace_nans (bool) – If
True, replace nans by 0
Returns: Return a tensor with shape Bx9xDxHxW where every voxel is the matrix logarithm of the inpur matrix at the same spatial location.
Return type: - Example:
import torch from torchvectorized.utils import sym from torchvectorized.vlinalg import vLogm b, c, d, h, w = 1, 9, 32, 32, 32 inputs = sym(torch.rand(b, c, d, h, w)) output = vLogm(inputs)
-
torchvectorized.vlinalg.vTrace(inputs: torch.Tensor)¶ Compute the trace of every voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.
Parameters: inputs (torch.Tensor) – The input tensor of shape Bx9xDxHxW, where the 9 channels represent flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices. Returns: Return a tensor with shape Bx1xDxHxW where every voxel is the trace of the inpur matrix at the same spatial location. Return type: torch.Tensor - Example:
import torch from torchvectorized.utils import sym from torchvectorized.vlinalg import vTrace b, c, d, h, w = 1, 9, 32, 32, 32 inputs = sym(torch.rand(b, c, d, h, w)) output = vTrace(inputs)
-
torchvectorized.vlinalg.vDet(inputs: torch.Tensor)¶ Compute the determinant of every voxel in a volume of flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices of shape Bx9xDxHxW.
Parameters: inputs (torch.Tensor) – The input tensor of shape Bx9xDxHxW, where the 9 channels represent flattened 3x3 symmetric matrices. Returns: Return a tensor with shape Bx1xDxHxW where every voxel is the determinant of the inpur matrix at the same spatial location. Return type: torch.Tensor - Example:
import torch from torchvectorized.utils import sym from torchvectorized.vlinalg import vDet b, c, d, h, w = 1, 9, 32, 32, 32 inputs = sym(torch.rand(b, c, d, h, w)) output = vDet(inputs)